Appearance
Permittivity of random ellipsoid structure
For details about the effective dielectric permittivity calculation, please see here.
Overview
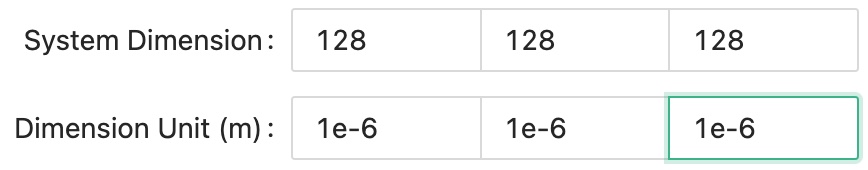
First, we will setup a cubic simulation with 128 microns along each dimension, that is 128 simulation grids times 1 micrometer for each grid.
Next, we will add two phases into the system, one for the matrix with lower permittivity, and the other for the embedded particle with higher permittivity.
Lastly, we will setup a structure with random ellipsoid for the composite material.
Step 1: Fill Input
Follow the introduction to the input part in the user manual and make sure you fill all of the blank boxes in the following four sections.
Dimension
Output
Choose vti for the output format, since we may want to visualize with Paraview.
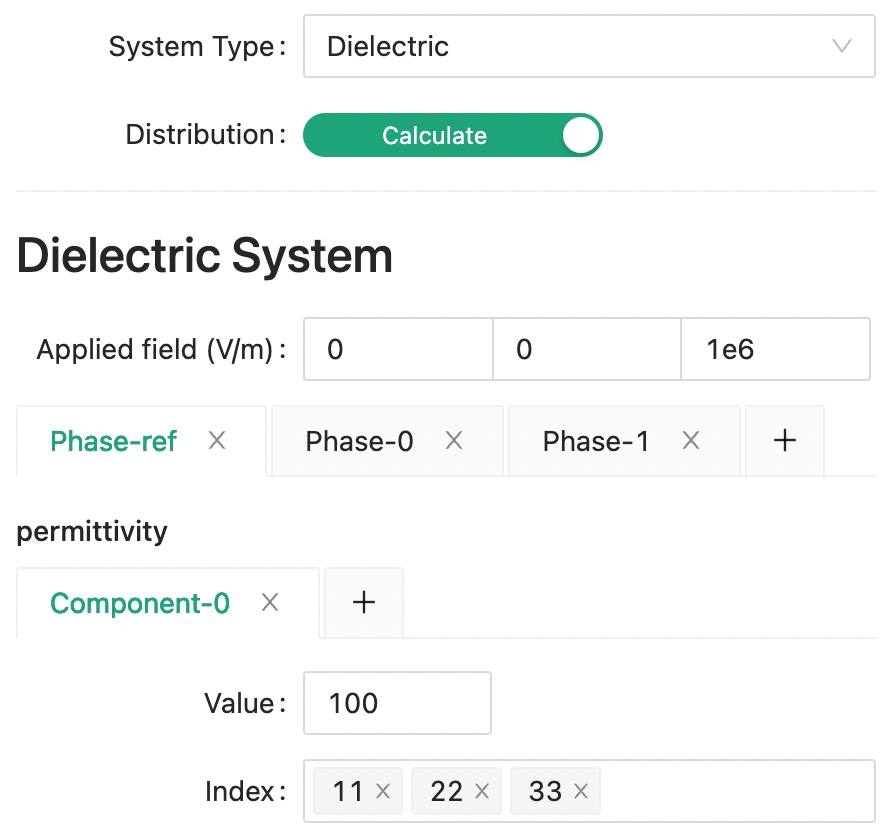
System
Choose "Dielectric" system for the System Type. Besides from the effective properties of dielectric permittivity, we also want to calculate a field distribution on external applied electric field, so we need to turn on the Distribution switch and set an Applied field value.
Next, set the reference permittivity value to be used in our solver.
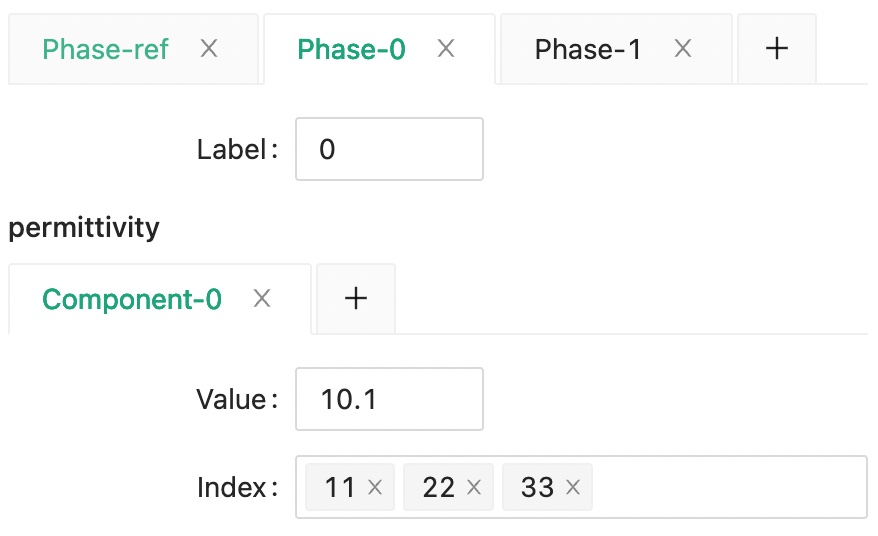
Then, set the low permittivity matrix phase as phase 0.
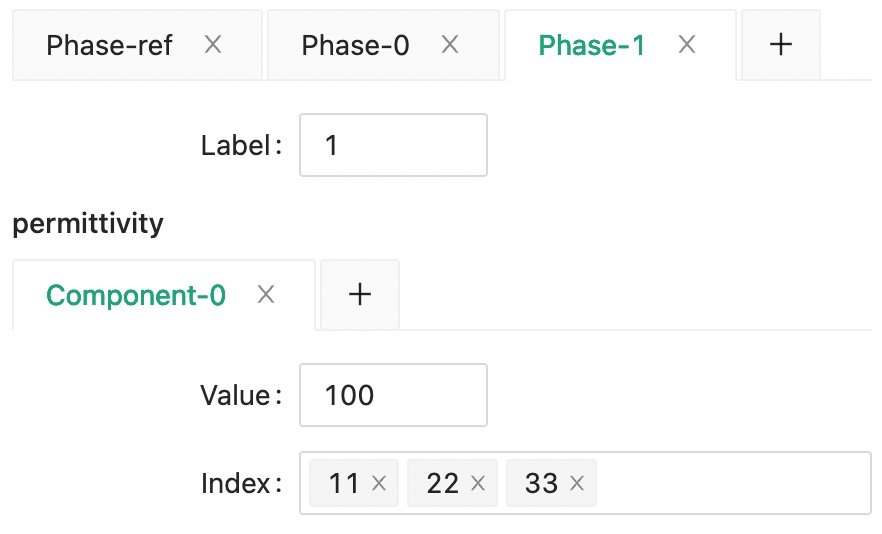
And the high permittivity embedded phase as phase 1.
Structure
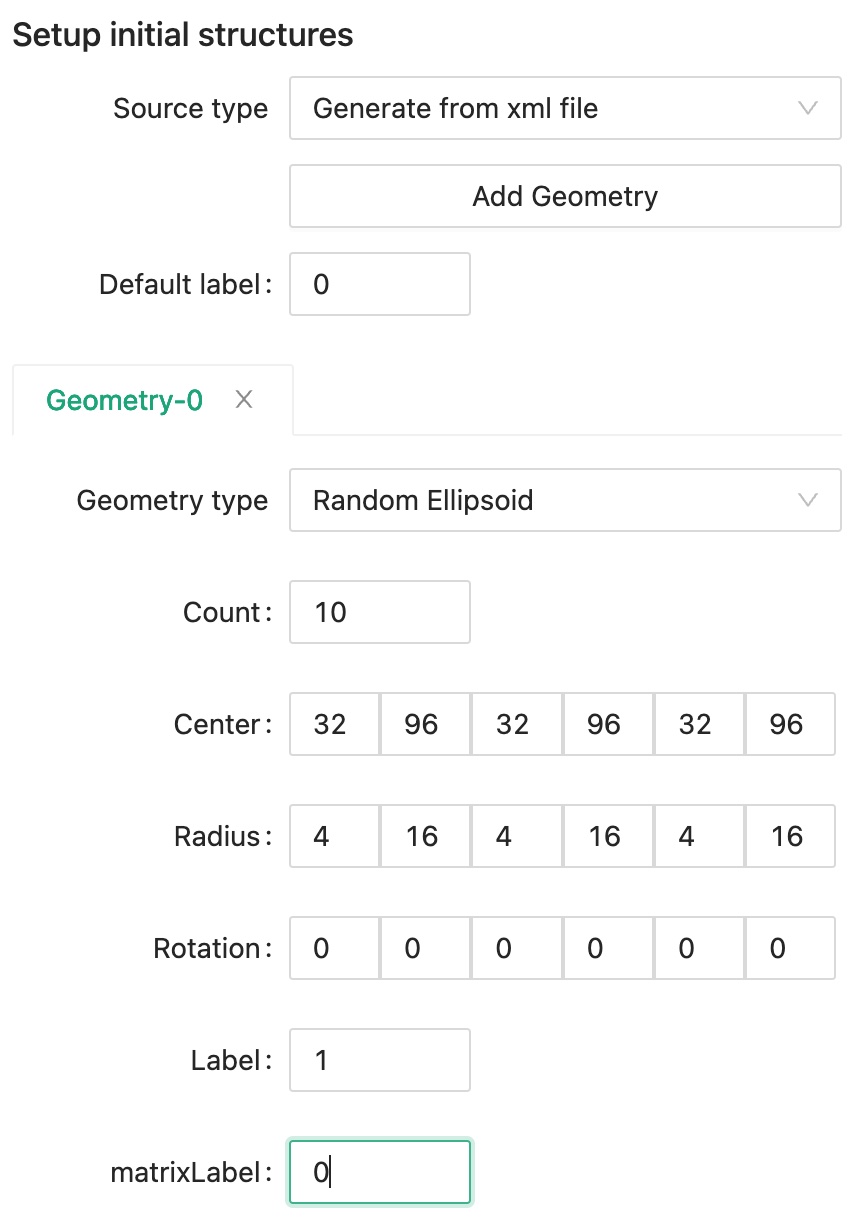
Since we want to generate the structure within the effective properties simulation program, we should choose "Generate from xml file" for the Source type.
Click Add Geometry button to create a new geometry tab, and set label 0 as the Default label.
We want to create 10 randomly generated ellipsoids whose centers are within the 32~96 grid points cubic box.
The ellipsoid radius is random value between 4 to 16 grid points, and there is no rotation added to the ellipsoid.
We will assign phase label 1 to this newly defined geometry and set its matrix label to be phase 0.
Step 1.5: Or Import Input
If you don't want to enter all of the values manually, you may import the following input file directly into the software.
Save the following content into a local file, then click the File -> Import in the menu to read your saved file.
<input>
<dimension>
<nx>128</nx>
<ny>128</ny>
<nz>128</nz>
<dx>1e-6</dx>
<dy>1e-6</dy>
<dz>1e-6</dz>
</dimension>
<output>
<format>vti</format>
</output>
<system>
<type>dielectric</type>
<distribution>1</distribution>
<external>
<electricField>
<x>0</x>
<y>0</y>
<z>1e6</z>
</electricField>
</external>
<solver>
<ref>
<tensor>
<name>permittivity</name>
<rank>2</rank>
<pointGroup>custom</pointGroup>
<component>
<value>100</value>
<index>11</index>
<index>22</index>
<index>33</index>
</component>
</tensor>
</ref>
</solver>
<material>
<phase>
<label>0</label>
<tensor>
<name>permittivity</name>
<rank>2</rank>
<pointGroup>custom</pointGroup>
<component>
<value>10.1</value>
<index>11</index>
<index>22</index>
<index>33</index>
</component>
</tensor>
</phase>
<phase>
<label>1</label>
<tensor>
<name>permittivity</name>
<rank>2</rank>
<pointGroup>custom</pointGroup>
<component>
<value>100</value>
<index>11</index>
<index>22</index>
<index>33</index>
</component>
</tensor>
</phase>
</material>
</system>
<structure>
<matrixLabel>0</matrixLabel>
<sourceType>xml</sourceType>
<geometry>
<type>ellipsoid_random</type>
<count>10</count>
<centerXMin>32</centerXMin>
<centerXMax>96</centerXMax>
<centerYMin>32</centerYMin>
<centerYMax>96</centerYMax>
<centerZMin>32</centerZMin>
<centerZMax>96</centerZMax>
<radiusXMin>4</radiusXMin>
<radiusXMax>16</radiusXMax>
<radiusYMin>4</radiusYMin>
<radiusYMax>16</radiusYMax>
<radiusZMin>4</radiusZMin>
<radiusZMax>16</radiusZMax>
<rotationXMin>0</rotationXMin>
<rotationXMax>0</rotationXMax>
<rotationYMin>0</rotationYMin>
<rotationYMax>0</rotationYMax>
<rotationZMin>0</rotationZMin>
<rotationZMax>0</rotationZMax>
<label>1</label>
<matrixLabel>0</matrixLabel>
</geometry>
</structure>
</input>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
Step 2: Export Input
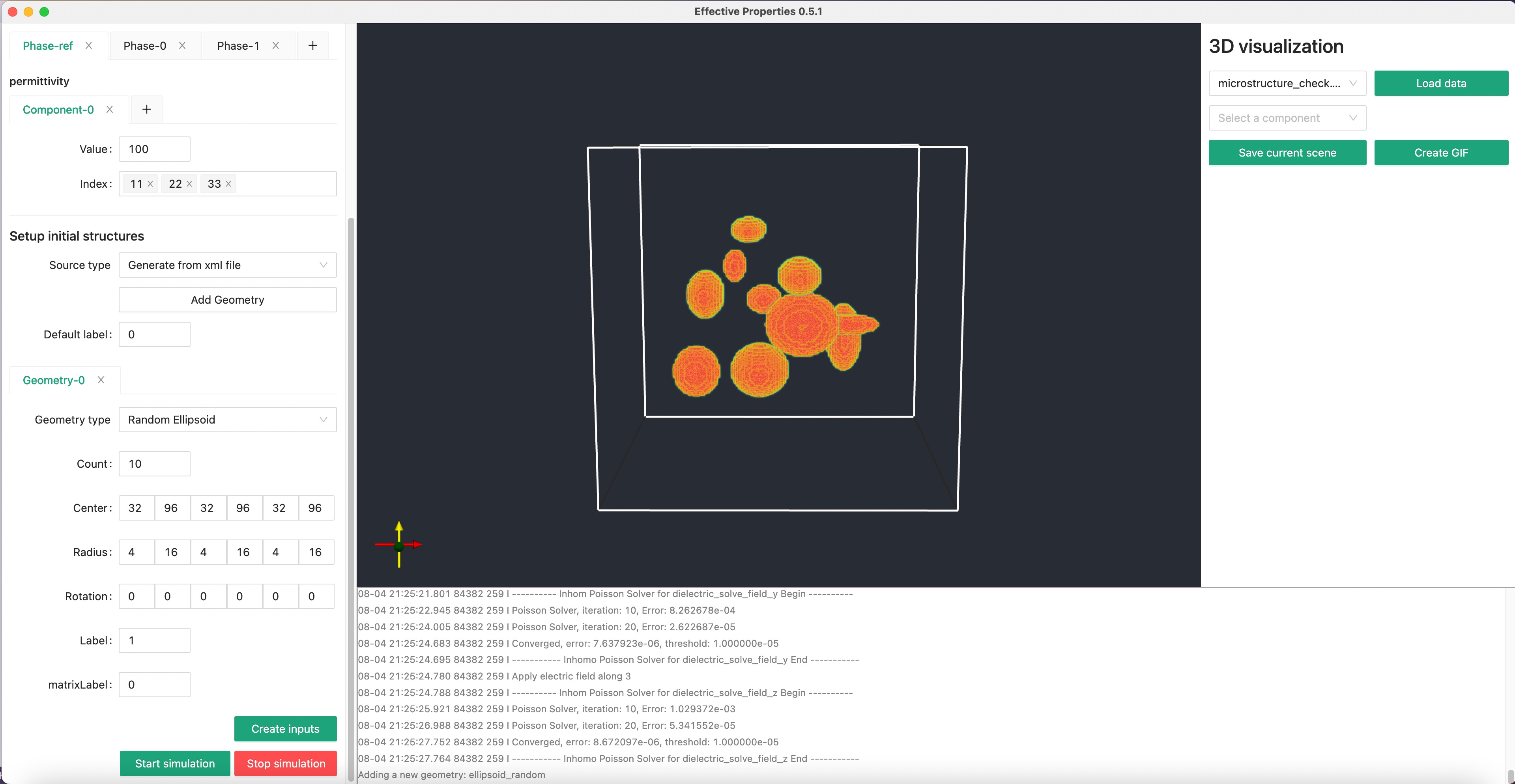
Click the Create Inputs button. Select the folder that you want to run the simulation in, and create a file named input.xml.
This step is simple but very important because the input.xml file is a prerequisite for starting any calculation.
Step 3: Run calculation
Make sure you have finished Step 2, you have to click the Create Input button, because it will both export the input.xml file and set the current working directory to that folder.
Then, you can click the Start simulation button to start the calculation. If you have not click the Create Input button and create the input.xml file, nothing will happen because the program does not know where to look for the input.xml file.
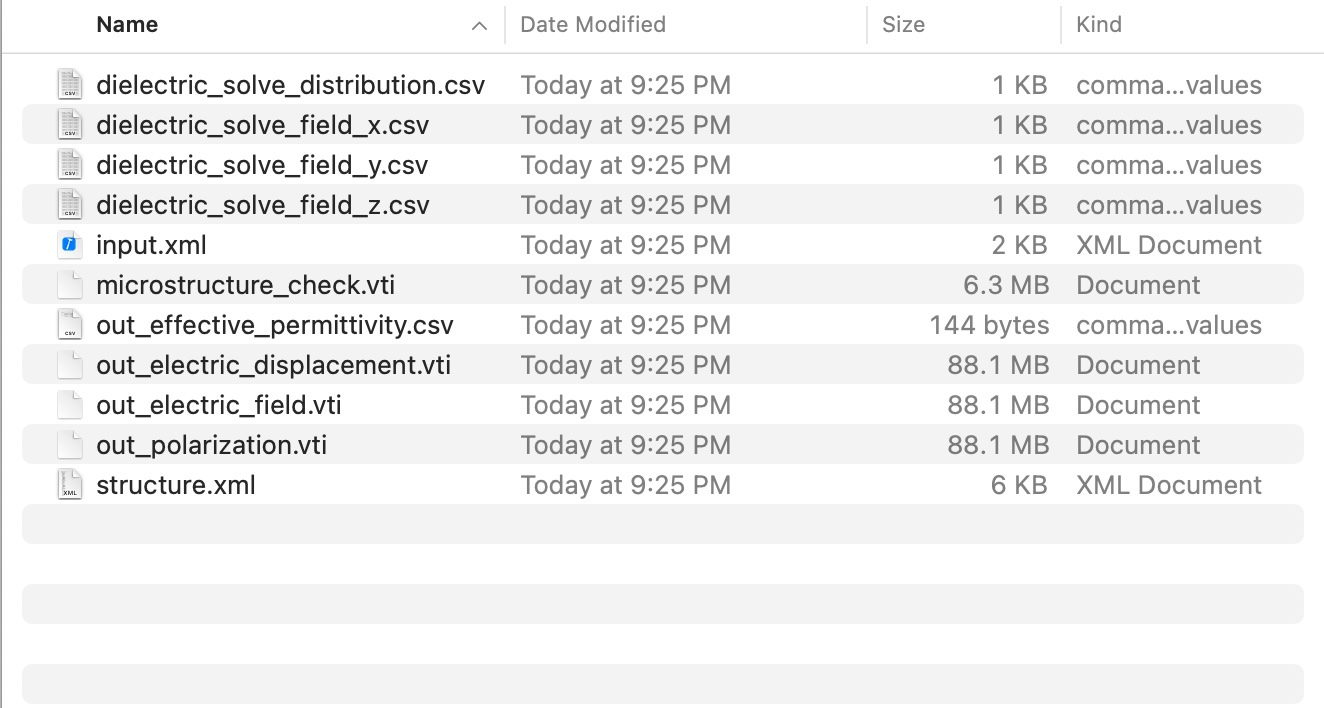
Step 4: Check Output
You will see the following output files in your simulation folder. Meaning for each of the files are explained in the Dielectric System.
Overall, there are two types of output data, vti files for 3D data, and csv files for tabular data.
Step 4.1: Check 3D data
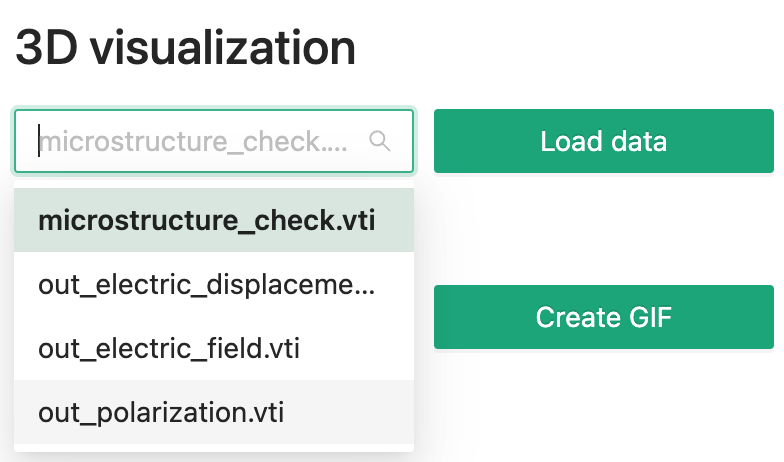
Within our software, you can quickly check a 3D vti data file.
Select the file you want to visualize using the dropdown menu, then click Load data button.
Then you will see something like this.
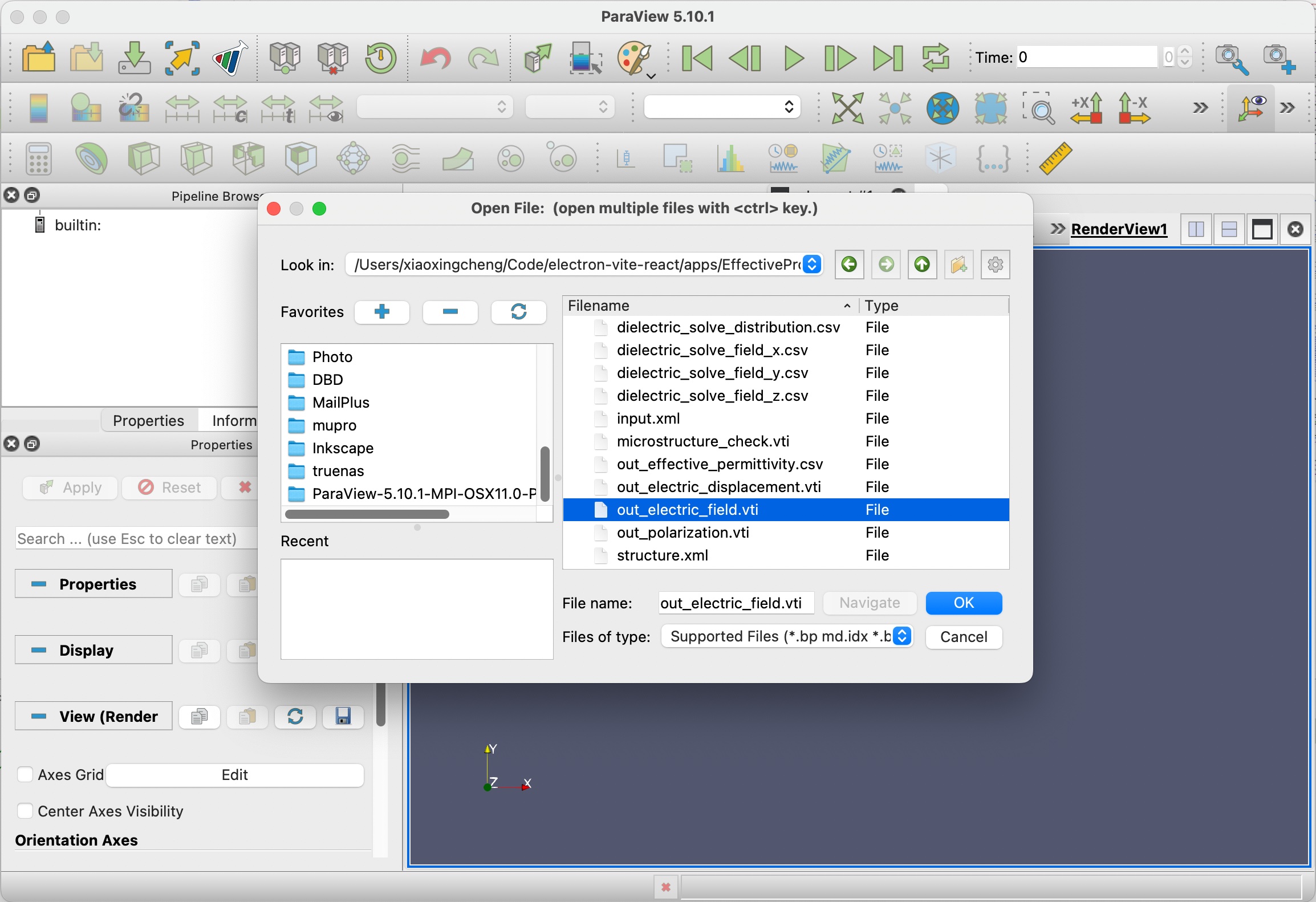
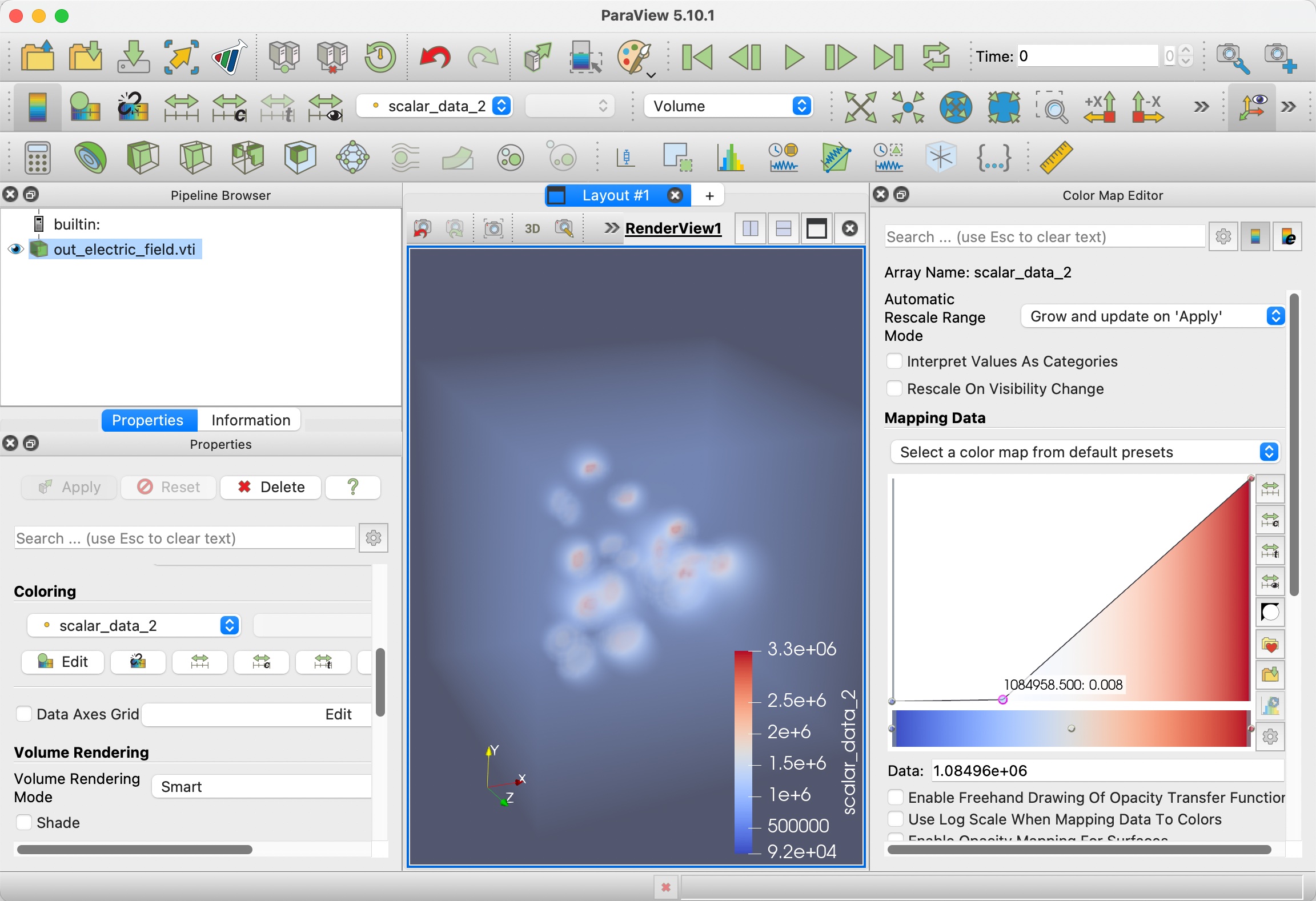
Step 4.2: Paraview
Next, we can try visualizing other files with Paraview. Click the first Open icon in the tool bar.
After the data is loaded, click Apply, then switch to Volume rendering and choose scalar_data_2, which is electric field along z for visualization.
We also need to tune the color lookup table to add some transparency to the data.
Step 4.3: Check tabular data
Though 3D data looks cool, the more important thing probably is still the effective permittivity, out_effective_permittivity.csv.
| Index | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +1.052429e+01 | +3.109117e-03 | -1.018976e-02 |
| 2 | +3.065335e-03 | +1.051951e+01 | +2.054915e-02 |
| 3 | -1.037035e-02 | +2.120530e-02 | +1.056976e+01 |